detoxification
glutathione
protein
protein intake
protein requirements
protein sysnthesis
whey
whey protein
whey protein concentrate
whey protein islolate
whey protein isolate
wpc
wpi

5 Surprising Benefits of Whey Protein
What's in this article:
- What is whey protein?
- How much do you need?
- Types of whey protein
- Choosing the right one
- Amino acids
- Glutathione
- 5 Surprising Benefits of Whey Protein
What is Whey Protein?
Firstly, whey protein is much more than just protein. A quality whey protein is naturally packaged with an amazing amount of minerals, vitamins and other nutrients which have incredible biological effects on the body.
There are different types of whey protein and some are better than others, which is important to understand, that not all whey protein is created equal. Whey protein concentrate is the best option that retains mother nature's perfect formula, bringing with it essential nutrients to promote healthy living.
Whey protein is a complete source of protein containing 20 amino acids (11 non-essential and 9 essential amino acids and are discussed in more detail below).
A quality whey protein is bioavailable, easy on the stomach, easy to absorb, healthy and a great way to help meet your daily protein requirements.
Is Whey Protein Gluten Free?
Yes, whey protein is gluten free. However, it must both be processed in a gluten free facility (such as Life Grip Protein) and the product must not contain or be blended with any other ingredients that contain gluten.
Most products today have it clearly positioned on the nutritional label if the product contains any gluten or is gluten free.
Anyone on a strict gluten free diet can be happy to know Life Grip Australian Grass Fed Whey Protein Powder is 100% gluten free. Additionally, here is a link to Coeliac Australia for additional information on gluten free living, research, studies and other information about gluten free lifestyles.
Yes, you can live your gluten free lifestyle and effortlessly achieve your daily protein requirements with one scoop of Life Grip Protein as a protein shake, a protein smoothie or adding to any baked goods.
What does Whey Protein do for your body?
You really are what you eat. The body you reside in today, has been rejuvenated, repaired and built from the nutrients absorbed from the meals you have eaten.
Furthermore, protein builds your tissues, hair, skin, nails and muscles, hence why it is important to consume healthy meals, with healthy sources and amounts of protein.
- Repairs, rejuvenates, rebuilds, tissues, hair, skin, nails and muscles (protein synthesis).
- Effortlessly meet your daily protein requirements.
- Supplies the body with essential amino acids involved in many bodily functions.
- Boosts and keeps your immune system strong.
- Supplies Glutathione precursors for optimal detoxification.
Whey protein has many benefits for your body and your overall well being and best of all, it is both simple to include in your daily diet and is easily absorbed. Efficient protein absorption is absolutely critical to optimal health.
When you compare to the equivalent amount of meat consumed to get the same protein amount from one serve of whey protein, your body can more easily break down, metabolise and absorb the nutrients and amino acids (we’ll get these in a moment) through the wall of the small intestine and into your bloodstream from whey.

Should I still eat meat and other protein sources?
Yes. It is best to consume a variety of protein sources to ensure you’re receiving a wide range of nutrients, micronutrients and amino acids from each protein source. In addition to a healthy diet, one to two scoops of whey protein is generally sufficient to help you meet your daily protein requirements.
Each scoop of Life Grip Protein has a highly absorbable (bioavailable) 21g of protein in every single scoop.
Can it help me detox and look younger?
Guess what? Your body's natural ability to detoxify is actually very, very good, as long as you’re treating your body and mind well through healthy living.
Consuming healthy meals with quality sources of protein, carbs and fats, supported with daily exercise (both essential for healthy living), means your skin can feed on the nutrients (including healthy fats) you provide this amazing organ and is rejuvenated and rebuilt with the support of healthy sources of protein.
To further assist your body's natural ability to detoxify, consume nutrient-dense foods and a high quality grass fed whey protein concentrate that contains Glutathione (the body's master antioxidant) precursors for healthy production of glutathione.
More on this below in Benefit #5: Boost Glutathione.
What are the types of Whey Protein?
There are 3 main types of whey protein as a result of the processing that results in the final product. Whey protein concentrate (WPC), whey protein isolate (WPI) or hydrolysed whey protein (WPH).
Whey protein concentrate (WPC):
This is the rawest form of protein still retaining all the nutrients, immune boosting benefits and healthy fats that make whey protein the complete health promoting protein it is. However, not all protein is created equal….
You want a whey protein that’s derived directly from milk, not from cheese or the cheese making process which is the most common type of whey. Whey protein derived directly from milk, brings with it all those previously mentioned nutritional benefits.
Moreover, whey protein derived from grass fed milk is best and in particular, Australian grass fed milk, which then is cold temperature processed to ensure all the health and nutritional benefits are retained, giving you a complete, protein rich, non-denatured, nutrient-dense whey protein powder. Interestingly, you can find this here.
Whey Protein Isolate (WPI):
Again, you want your whey isolate to be derived directly from milk, however, in most cases, your WPI is a byproduct from the cheese making process. Whey protein isolate is the second form of whey protein after whey concentrate which has been stripped of many of the nutritional and immune boosting benefits, including the healthy fats, which together, are there to help with important things like….absorbability.
Many believe whey isolate is free of, or much lower in carbohydrates than a whey concentrate, however, when comparing nutritional labels between both, you’ll notice there’s almost no difference.
Furthermore, you’ll notice digestive enzymes added to most whey isolates to help with absorbability, which is not needed with a high quality grass fed whey protein concentrate that retains all the beneficial nutrients.
Hydrolysed Whey Protein (WPH):
This is the next form of whey protein broken and processed in a further step. Hydrolysed just means the protein is in a sense, ‘pre digested’ with all amino acids broken apart to assist with absorption. Thus, leaving you with just protein, stripped of the nutrients similar to the isolate.
This is not to say whey isolate or hydrolysed whey protein is bad, it just means if you’re taking a whey protein for high absorbability, immune boosting benefits, glutathione production, healthy fats and the micronutrients that make grass fed whey concentrate one of the richest sources of protein on the planet, you will forgo all these benefits.
Another important consideration, is the nutrients and healthy fats packaged with whey protein concentrate derived from Australian grass fed milk, actually make it bioavailable for better absorption, putting your whey protein to work quickly and efficiently, without the need for additional digestive enzymes or processes.
Basically, a non-denatured, whey protein concentrate derived from grass fed milk is still packaged as nature intended, to work with your normal bodily processes. Life Grip Protein is a whey concentrate that’s non-denatured and derived from the grass fed milk of Australian grass fed dairy cows.
It is important to note, most whey protein powders are both derived from the cheese making process and from the dairy of grain fed cows. The best protein is whey concentrate, derived from the milk of Australian grass fed dairy cows.
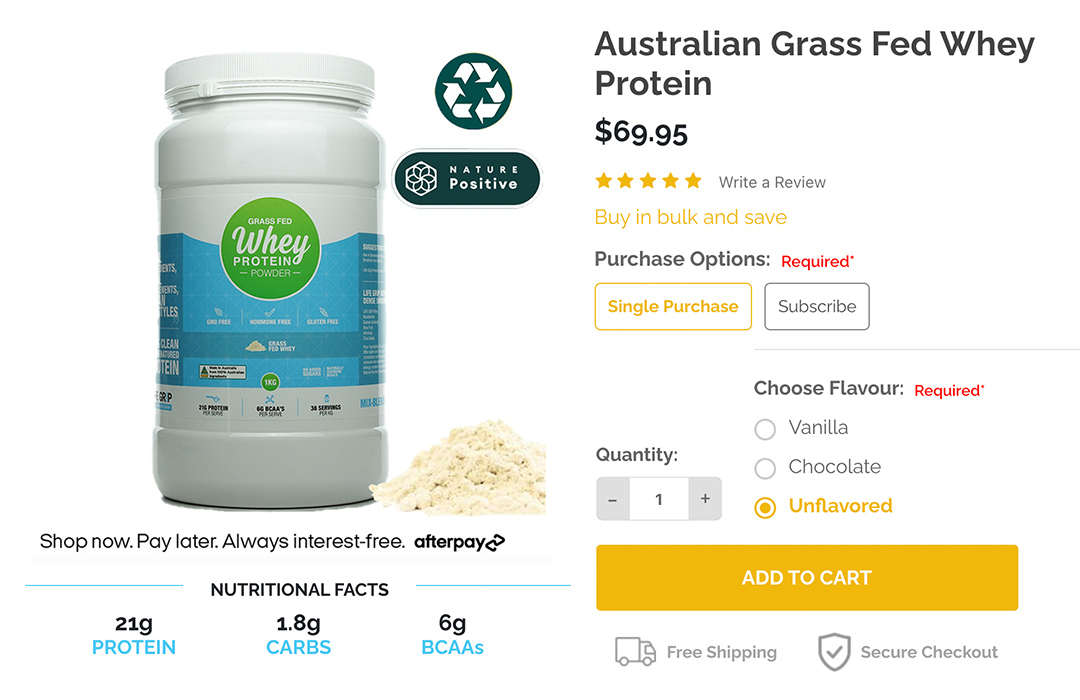
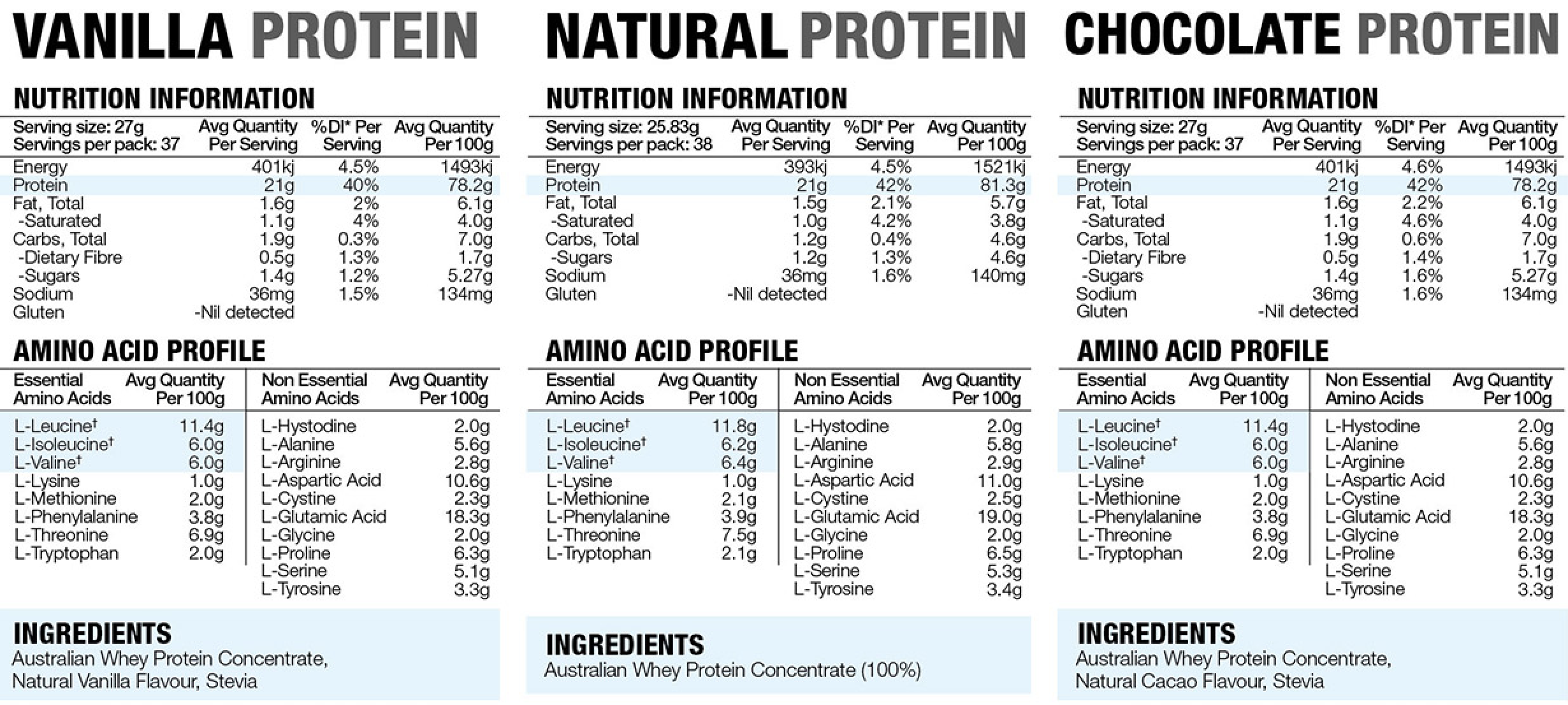
Nutritional facts of Whey Protein:
The richest source of protein on the planet, whey protein concentrate, derived from grass fed milk, contains a complete source of protein with all essential amino acids, micronutrients, healthy fats, glutathione precursors and immune boosting benefits.
Below you'll see the nutritional tables for all three flavours of Life Grip Protein.
Amino acids:
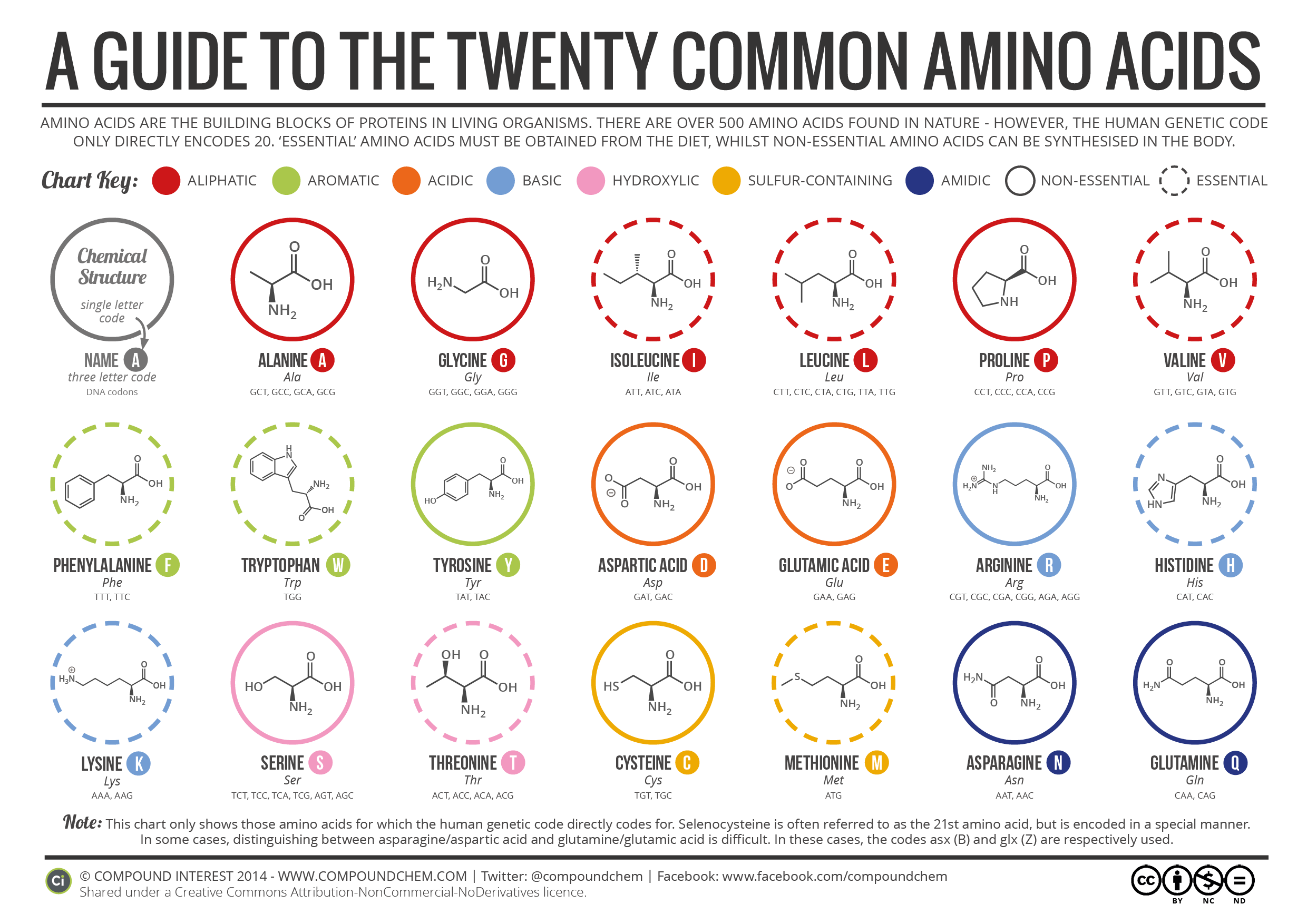
A complete protein has 20 amino acids and are the building blocks of protein. Each time you consume protein, your body breaks it down into its simplest form, which are amino acids, which are then absorbed into the bloodstream.
The separated proteins into amino acids get put back together by your body to then rebuild and rejuvenate your muscles, tissues, skin, hair, nails and assist in various other processes in the body.
You have essential and non-essential amino acids. Essential amino acids mean that our body doesn’t make them so we need to get them from our diet (from food). Non-essential amino acids mean our body already makes them. Here’s a list of the amino acids below;
Essential amino acids:
Histidine, isoleucine, leucine, lysine, methionine, phenylalanine, threonine, tryptophan, and valine.
Non-essential amino acids:
Alanine, arginine, asparagine, aspartic acid, cysteine, glutamic acid, glutamine, glycine, proline, serine, and tyrosine.
Healthy Fats:
Grass fed whey protein concentrate contains healthy levels of both omega-3 fatty acids (unsaturated) and CLA (conjugated linoleic acid). Omega-3’s are good for the body, brain, blood and the heart. This healthy fat combined with CLA, is another reason a grass fed whey protein concentrate is good for you.
According to Alothman et al. (2019), significant variation in a milks macronutrients (fat and protein) and micronutrients (vitamins, minerals, fatty acids, amino acids) are caused through differences in feeding regimen.
Furthermore, significant increases in concentrations of conjugated linoleic acid (CLA) and unsaturated (omega 3) fatty acids were reported in the milk of pasture fed (grass fed) cows compared with typical grain fed cattle (Alothman et al., 2019).
Does whey protein have vitamins and minerals?
Yes. In fact, fresh pasture (grass) as the main source of nutrition for cows to feed on, provides the vitamins, minerals and antioxidants that are essential for the animals health and are transferred to the milk (Alothman et al., 2019).
What vitamins are in whey protein?
A high quality whey protein contains a large range of micronutrients to support the mind, body and optimal health.. Rich in the B complex vitamins such as B1 Thiamin, B2 Riboflavin, B3 Niacin, B5, B6 and Vitamin B12, including Folate and Choline.
What minerals are in whey protein?
A high quality whey protein is rich in minerals your body and mind require for optimal health. These minerals include, Selenium, Phosphorus, Zinc, Magnesium, Copper, Potassium, Iron, Calcium and Sodium.
Is whey protein a powder?
Yes. This is an easy to absorb source of protein, bringing with it a range of nutritional and immune boosting benefits. A high quality whey protein will mix well.
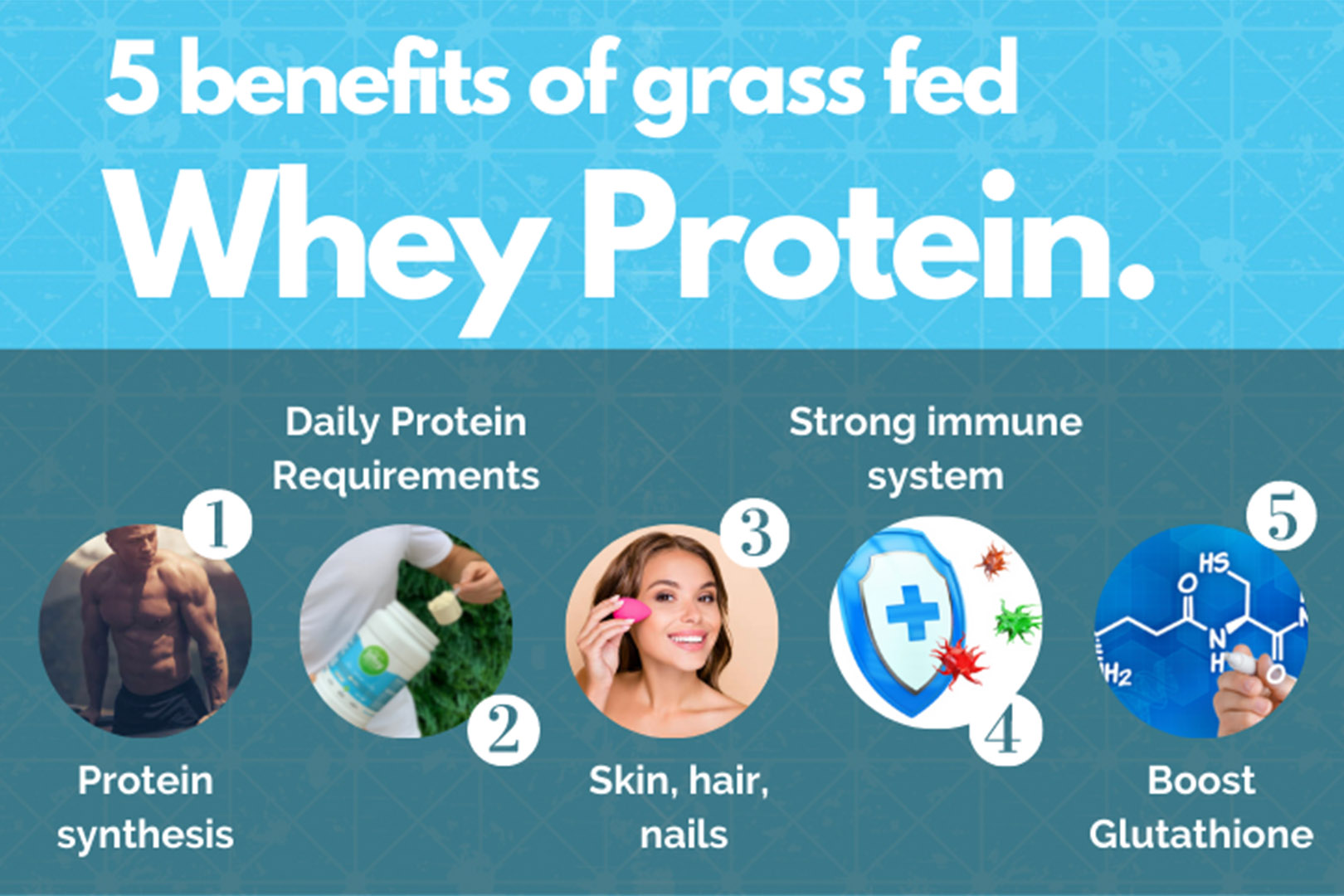
Now that we’ve explained whey protein, the types of whey protein and what makes a high quality whey protein, let’s dive into the 5 surprising benefits of whey protein.
Benefit #1: Bioavailable protein solution for maintaining, and building lean muscle mass.
When it comes to a great looking body, lean muscle mass positioned under a healthy body fat percentage, creates a look you can be proud of when you look at the work you put in week in and week out.
The definition of your muscles are important for a couple of reasons. When you can see the definition of your muscles, you are more than likely living with a healthy level of body fat. Not too much that you can’t see your muscles and not too little that your skin is so tight your muscles look like they are shrink wrapped.
When body fat is too low, you’ll notice your hormones are out of balance, you’re more than likely irritable or have a short fuse and experience brain fog. A healthy amount of body fat is great for your health, longevity and that light, energised feeling and a feeling of self confidence your active lifestyle is working.
So good on you, keep moving forward, stay healthy and do those things that bring you joy.
Benefit #2: Quality source of protein to effortlessly meet your daily protein requirements.
A healthy daily protein intake varies for everyone depending on the amount of lean muscle mass, how active you are (including what type of activity) and your health goals, not to mention state of health and wellbeing. But a common question is where do I start? Let’s cover this below.
How much protein?
A healthy place to begin your protein intake is 0.8g per kg of body weight (Phillips, 2006) and up to 1.2g of protein per kg of body weight for most individuals. Furthermore, increasing your protein intake from 0.8g towards 1.2g per kg of bodyweight as your activity level increases.
What about heavy exercise, weight training, HIIT, F45 and Crossfit?
A place to begin is 1.2g of protein per kg of bodyweight, increasing towards 2.0g of protein per kg of body weight as individually required and level of training intensity.
How much protein for intense training?
Lifting heavy weights, HIIT and intense endurance training such as Ironman, triathlon training, swimming, running and cycling requires a higher protein intake than most people. For those who are training heavy or twice daily 5 - 7 times per week, require a protein intake in the range of 1.2 to 2.0g of protein per kg of body weight (Jäger, 2017).
Whey protein is a great solution to help meet your daily protein requirements, rather than attempting to get it all from meat sources, which for many people is difficult to do and not to mention takes a lot of energy to metabolise.
Furthermore, many people just don’t want to feel like they’re eating all the time. Additionally, many people follow a TRE (time restricted eating) plan or an IF (intermittent fasting) protocol and whey protein powder is a great solution.
When training hard, recovery is where the magic happens and a high quality whey protein concentrate is option to optimise recovery and easier for your body to metabolise a protein powder, rather than meat (especially post workout).
An easy solution is adding one scoop of Life Grip Protein to your daily routine to provide an optimal 21g of complete protein that’s easy on the stomach, highly bioavailable and easy to add to smoothies, baked good or in a simple protein shake.
TIP:Try a scoop of Life Grip Protein in 250ml icy cold coconut water post exercise. You'll get your 21g of protein and a natural balance of electrolytes to restore and recover quicker, post exercise.
Benefit #3: Quality whey protein supports healthy skin, nails, hair and well defined lean muscle.
Lean muscle, skin, hair and nails, built from healthy foods and high quality sources of protein, supported by a clean, healthy lifestyle, over time, stands out.
People notice the glow in the face and skin, the muscle definition and healthy strong nails and full coloured healthy hair. When it comes to healthy looking skin, glutathione is critical, along with supporting your body’s natural collagen.
Did you know, peptides from high quality grass fed whey protein prevented type IV Collagen (the most abundant, structural component of tissue) degradation (Patel, 2015).
Furthermore, according to Patel (2015), results demonstrate considerable protection against UV-irradiated skin aging, to support healthy skin.
Important to note as getting out in the sun each day is an important part of a healthy lifestyle. Sun on the skin and in your eyes each day is crucial for optimal health and wellbeing (including sleep. More on the sun and sleep here.
Benefit #4: Help boost your immune system.
Our body’s immune system is something to be thankful for each day. It fights off various bacteria, infections, viruses to ensure we’re feeling our best. It is important to do our best to live healthy by eating healthy meals with nutrient dense foods and exercise each day, not to mention drink sufficient amounts of clean water.
However, some foods can really boost your immune system, keeping it strong and you healthy. Let’s talk about Immunoglobulins...
Does whey protein contain Immunoglobulins?
Yes. A high quality grass fed whey protein contains what are called Immunoglobulins, also known as antibodies that your immune system creates.
A daily serving of a high quality grass fed whey protein concentrate can help with healthy levels of immunoglobulins. In addition to immunoglobulins, whey protein contains a number of bioactive components such as alpha-lactalbumin, lactoferrin and beta-lactoglobulin (Gupta et al., 2016).
Lactoferrin:
In short, lactoferrin is an anti-microbial and anti-inflammatory agent and possesses the unique ability to induce the activity of macrophages, natural killer cells and colony stimulating factor. Here’s what these are below;
- Macrophages are white blood cells that remove dead cells and stimulate the action of other immune cells.
- Natural killer cells (NK cells) kill virally infected cells.
- Colony stimulating factor are proteins that stimulate the production of more immune cells.
Immunoglobulins:
Immunoglobulins are proteins that enhance immunity and exist as antibodies in whey protein which are beneficial in the treatment of various infections (Gupta et al., 2016). These immunoglobulins include IgG1, IgG2, IgA and IgM and survive the passage through the stomach to intestines and provide an antimicrobial action in the intestinal tract (Gupta et al., 2016).
Benefits #5: Boost Glutathione and optimise your body's natural ability to detoxify.
When it comes to your body's natural ability to detoxify, one cannot overlook the importance of both living a clean, healthy lifestyle and the body’s master antioxidant, Glutathione.
Glutathione is a sulfur, which is a sticky substance that binds to toxins, metals and free radicals to allow your liver to process these and safely excrete them from the body.
Glutathione is present in all cells, so much so that in healthy amounts, according to Pizzorno (2014), is equivalent to the cellular concentrations of glucose, cholesterol and potassium.
In contrast, low levels of glutathione caused by depletion, ultimately triggers a process called apoptosis, which is in other terms, programmed cell death (Pizzorno, 2014).
How can I increase Glutathione?
Thankfully, there are specific nutrients that can promote the healthy, natural production of glutathione within the body.
One such option is a high quality, grass fed whey protein concentrate that is rich in the amino acid Cysteine and is effective in raising blood concentration levels of glutathione (Pizzorno, 2014).
A grass fed whey concentrate really is a nutrition power house and easy to include in your daily diet without any dramatic changes to your lifestyle.
Ok, let’s recap this article and condense into something you can remember and simply put into practise.
The best whey protein is an Australian grass fed whey protein concentrate, you can find this here. You need an adequate amount of protein each day to provide the essential amino acids, the combined micronutrients, immune supporting immunoglobulins, healthy fats and the ever so critical glutathione precursors.
Not only will you feel the difference, you’ll be supporting your healthy lifestyle and be proud of the progress you’re making from all those healthy decisions you make everyday.
To be honest, the best decision I have personally ever made is choosing to live and clean, healthy lifestyle. I’m fairly confident there’s more people out there who agree it’s the best decision they’ve ever made.
If you have not transitioned into a clean, healthy lifestyle as yet and thinking about it, we would love to have you. We’ll help you find your intrinsic motivation and the information you need to create and live a fingerprint specific lifestyle, that you’re inspired to wake up and live everyday.
Information, support and assistance you won’t find anywhere else.
At Life Grip, we’re walking the same path with you. Living cleaner, healthier lifestyles.
References:
Alothman, M., Hogan, S. A., Hennessy, D., Dillon, P., Kilcawley, K. N., O'Donovan, M., Tobin, J., Fenelon, M. A., & O'Callaghan, T. F. (2019). The "Grass-Fed" Milk Story: Understanding the Impact of Pasture Feeding on the Composition and Quality of Bovine Milk. Foods (Basel, Switzerland), 8(8), 350. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods8080350
Gupta A, Jadhav JB, Gunaware KD, Shinde B (2016) Whey Proteins and Its Impact on Human Health Nutrition: Review. J Anal Pharm Res 3(8): 00083. DOI: 10.15406/japlr.2016.03.00083
Patel S. (2015). Emerging trends in nutraceutical applications of whey protein and its derivatives. Journal of food science and technology, 52(11), 6847–6858. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-015-1894-0
Pizzorno J. (2014). Glutathione!. Integrative medicine (Encinitas, Calif.), 13(1), 8–12.
Phillips S. M. (2006). Dietary protein for athletes: from requirements to metabolic advantage. Applied physiology, nutrition, and metabolism = Physiologie appliquee, nutrition et metabolisme, 31(6), 647–654. https://doi.org/10.1139/h06-035
about us
Our focus goes into the products we pro- duce in order to increase your quality of life. While other companies are focused on glamour, fashion and fitness models, we’ll still be here creating the cleanest supplements on the market.
A brand built on quality, virtue, convenience and a minimalistic focus to retain mother na- tures perfect formula, for us all to reap the benefits. At Life Grip we Eat, Think & Live Clean.
get updated
stay updated & subscribe to our newsletter
recent posts
like us on facebook