protein intake
protein powder
rdi protein
serving size
whey protein
wpc

How much protein do I need?
How much protein do I need?
You need enough protein to support wellbeing, the multitude of work protein does in the body, maintain and rejuvinate your muscle mass, tissues, hair, skin, nails and bone mass.
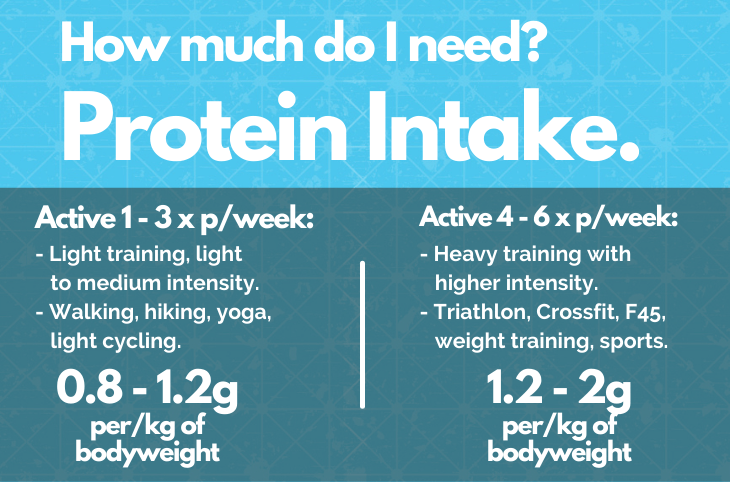
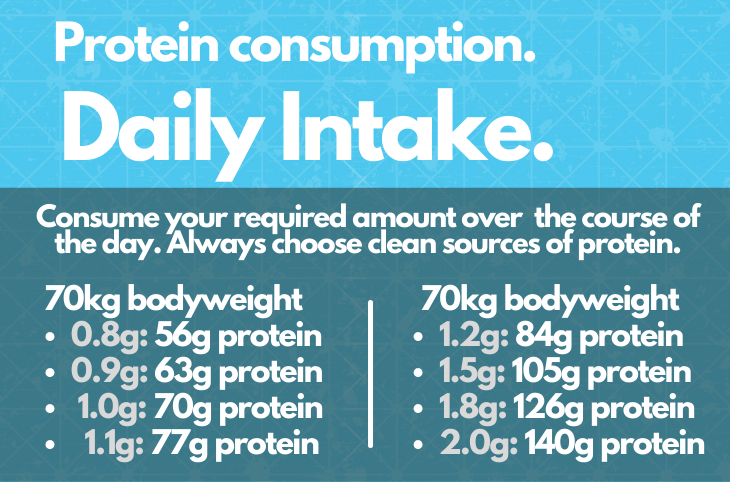
A healthy place to begin your protein intake is 0.8g per kg of body weight (Phillips, 2006) and up to 1.2g of protein per kg of body weight for most individuals. Furthermore, increasing your protein intake from 0.8g towards 1.2g per kg of bodyweight as your activity level increases.
How much protein for heavy and strenuous exercise?
Firstly, what is heavy exercise...this is exercise such as weight training, crossfit, F45 and group fitness (metabolic conditioning) workouts, including heavy exercise such as Ironman and Triathlon training. However, heavy exercise is any form of strenuous training and the frequency, duration and intensity must be taken into account. A place to begin is 1.2g of protein per kg of bodyweight, increasing towards 2.0g of protein per kg of body weight as individually required and level of training intensity.
How much protein for intense training?
Lifting heavy weights, HIIT and intense endurance training such as Ironman, triathlon training, swimming, running and cycling requires a higher protein intake than most people. For those who are training heavy or twice daily 5 - 7 times per week, require a protein intake in the range of 1.2 to 2.0g of protein per kg of body weight (Jäger, 2017).
Whey protein is a great solution to help meet your daily protein requirements, rather than attempting to get it all from meat sources, which for many people is difficult to do and not to mention takes a lot of energy to metabolise.
Furthermore, many people just don’t want to feel like they’re eating all the time. Additionally, many people follow a TRE (time restricted eating) plan or an IF (intermittent fasting) protocol and whey protein powder is a great solution.
When training hard, recovery is where the magic happens and a high quality whey protein concentrate is a brilliant option to optimise recovery and is easier for your body to metabolise a protein powder, rather than meat (especially post workout).
Boost your daily protein requirements with one scoop of Life Grip Protein every day.
Every scoop/serve has a generous 21g of complete protein, packed with nutrients to maintain and build lean muscle, hair, skin, nails and bone density. Life Grip Protein is derived from the milk of grass fed dairy cows that feed off bright green grass across pastured land, right here in Australia.
The nutrients from healthy grass fed milk is retained within the whey protein, providing you with not only a rich protein source, but with immune boosting and micronutrients that promote wellbeing and build a stronger you.
Strong is not just about lifting heavy weights and consuming lots of protein. It's having a strong body/mind, immune system, healthy gut and optimal detoxification. By ensuring your meeting your daily protein requirements, keeping active and consuming clean whole foods, you're giving yourself the best chance to optimal wellbeing and increasing your health span.
An easy solution is adding one scoop of Life Grip Protein to your daily routine to provide an optimal 21g of complete protein that’s easy on the stomach, highly bioavailable and easy to add to smoothies, baked good or in a simple protein shake.
TIP:Try a scoop of Life Grip Protein in 250ml icy cold coconut water post exercise. You'll get your 21g of protein and a natural balance of electrolytes to restore and recover quicker, post exercise.
Want to know more about the benefits of Life Grip whey protein?
Click on this article link to learn more - 5 Surprising Benefits of Whey Protein
References:
Jäger, R., Kerksick, C. M., Campbell, B. I., Cribb, P. J., Wells, S. D., Skwiat, T. M., Purpura, M., Ziegenfuss, T. N., Ferrando, A. A., Arent, S. M., Smith-Ryan, A. E., Stout, J. R., Arciero, P. J., Ormsbee, M. J., Taylor, L. W., Wilborn, C. D., Kalman, D. S., Kreider, R. B., Willoughby, D. S., Hoffman, J. R., … Antonio, J. (2017). International Society of Sports Nutrition Position Stand: protein and exercise. Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition, 14, 20. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12970-017-0177-8
Phillips S. M. (2006). Dietary protein for athletes: from requirements to metabolic advantage. Applied physiology, nutrition, and metabolism = Physiologie appliquee, nutrition et metabolisme, 31(6), 647–654. https://doi.org/10.1139/h06-035
about us
Our focus goes into the products we pro- duce in order to increase your quality of life. While other companies are focused on glamour, fashion and fitness models, we’ll still be here creating the cleanest supplements on the market.
A brand built on quality, virtue, convenience and a minimalistic focus to retain mother na- tures perfect formula, for us all to reap the benefits. At Life Grip we Eat, Think & Live Clean.
get updated
stay updated & subscribe to our newsletter
recent posts
like us on facebook